DUHOK
Home †|††DestpÍk††|††Ana Sayfa

Duhok yek ji bajarên Başûrê Kurdistanê ye, navenda parêzgeha Duhokê ye (herêma Badînan). Li gor hindek jêderan dîroka bajarê Duhokê vedigere 8000-12000 berî zayînê.
Gelek cihû jî li parêzgeha Duhokê hebûn lê di salên 1940an da hemû çûn Îsrailê. Duhok bajarek gelek spehî û rind e, li nav gelieykî di navbera du çiyayan de ye û du çem; Çemê Dihokê û çemê Hişke, di nav bajêr de diherikin. Duhok cîyeke stratejîkî ye û lii ser riya bazirganiyê bûye.
Têt gotin ku berê xala gumrikê bûye û l#e bac dähat wergirtin. Her karwanekî ku ji wê riyê derbas bibûya, diviya bac bidaya. Bac jî DU HOK bûn, ango DU MIST bûn. Lewra jê ra dibêjên Duhok (du + hok).

Since the Kurds were the earliest community founders (proto-clans) in historical Mesopotamia, they spread throughout Mesopotamia since the begining of the historical process. As Ferdinand Hennerbichler state: “Kurds are clearly visible from the earliest traceable beginnings as the indigenous people of the Neolithic, Northern Fertile Crescent lands of the Near East and Eurasia.” In this connection, as there are tribes derived from the Kurds, many tribes also lived among the Kurds. As the Kurds established their own kingdoms and empires such as the Gutians, the Mitanians, here were also Kurds in the kingdoms and empires of many other peoples, as in the Sumerians and the Hurrians. The Hurrians are one of these peoples, including the Kurds. This does not mean that even though the Hurians were from the Semitic race and were pledging allegiance to the gods and religions of other peoples, this does not mean that they were not the ancestors of the Kurds. There were also Kurds among the Hurrians as in the Sumerians, and these Hurri-Kurds are of course considered to be the ancestors of the Kurds. ___________________ Kürdler tarihi Mezopotanya'da en ilk toplum kurucuları (proto-kavim) oldukları için tarihi süreç içerisinde tüm Mezopotamya'ya yayılmaları gerçekleşmiştir. Ferdinand Hennerbichler'in dediği gibi: “kürdler izlenebilir en erken başlangıçtan beri Yakın Doğu ve Avrasya’nın Cilalı Taş Devri, Kuzey Bereketli Hilal topraklarının yerli halkı olduğunu açıkça görülmektedir.” Bu münasebetle kürdlerden türeme kavimler olduğu gibi, birçok kavim de kürdlerin içinde yaşamıştır. Kürdler gutiler, gutiler, mitaniler gibi kendi öz krallık ve imparatorluklarını kurdukları gibi, sümer'lerde ve huriler'de olduğu gibi birçok kavimin krallık ve imparatorluklarının içinde kürdler de olmuştur. Huriler de içinde kürdlerin bulunduğu bu kavimlerden biridir. Bu şu anlama gelmiyor, herne kadar huriler semitik ırkından gelme idiylerse de ve herne kadar başka kavimlerin tanrılarına ve dinlerine biat ediyordularsa da bu onların kürdlerin ataları olmadığı sonucunu getirmez. Hurilerin içinde sümerler'de olduğu gibi kürdler de vardı ve bu huri-kürdler elbette ki kürdlerin ataları sayılır. |

'Mezopotamya'da yaşayan Mard(Mardoilerin) bir Kürd Klanı'dır' Josef Markwart (1864-1930)
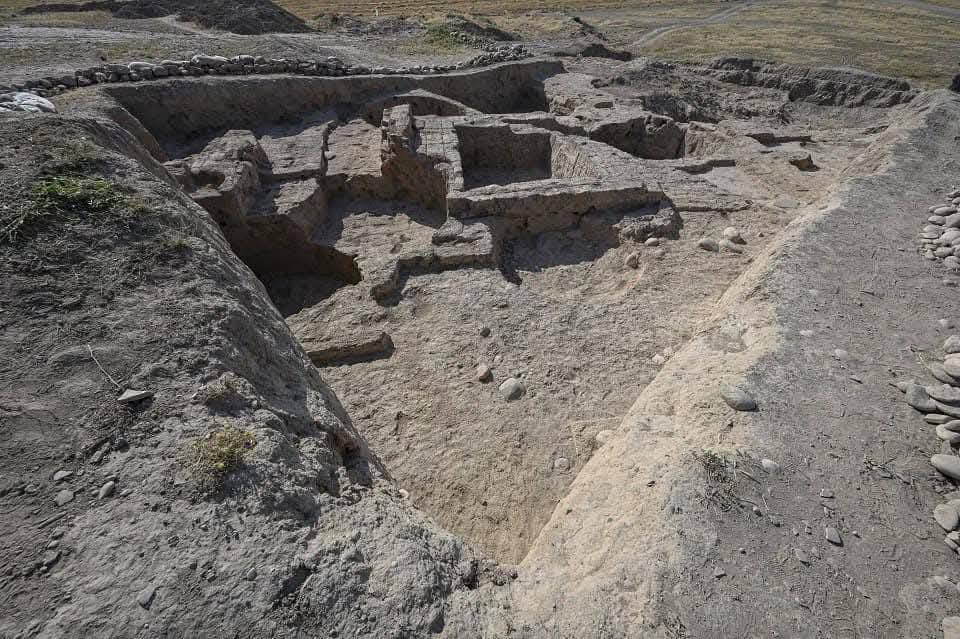
Mardiler antik çağda Duhok ve çevresinde yaşadılar. Son yıllarda Duhok’ta yapılan kazı çalışmalarında bir çok antik bulgu ve antik kent ortaya çıkarıldı.






Ala Kurdistanê boyax dike, Xwedê Wî star bike..



Nexweşxaneya Gulan

Nexweşxaneya Onkolojiyê

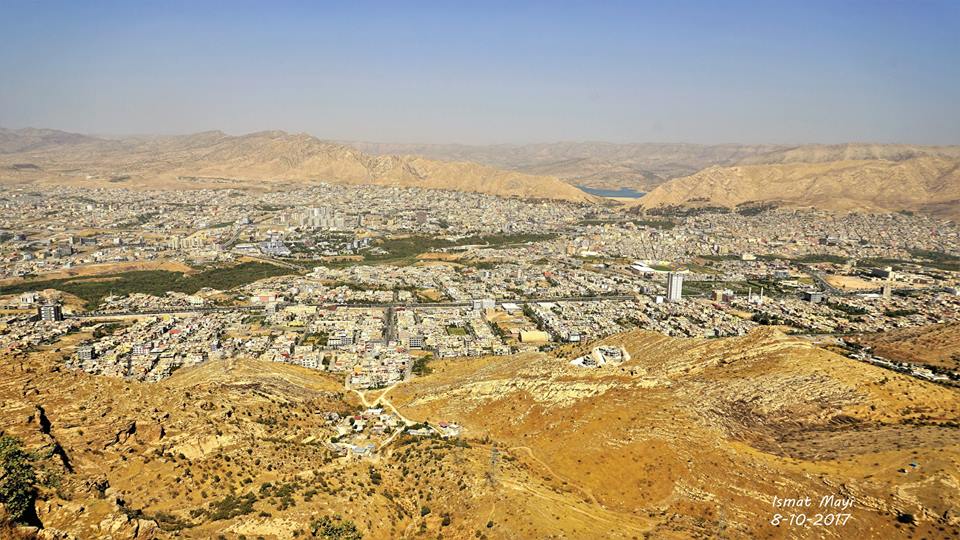
Kurdistan doğası harika bir TABLO gibidir.
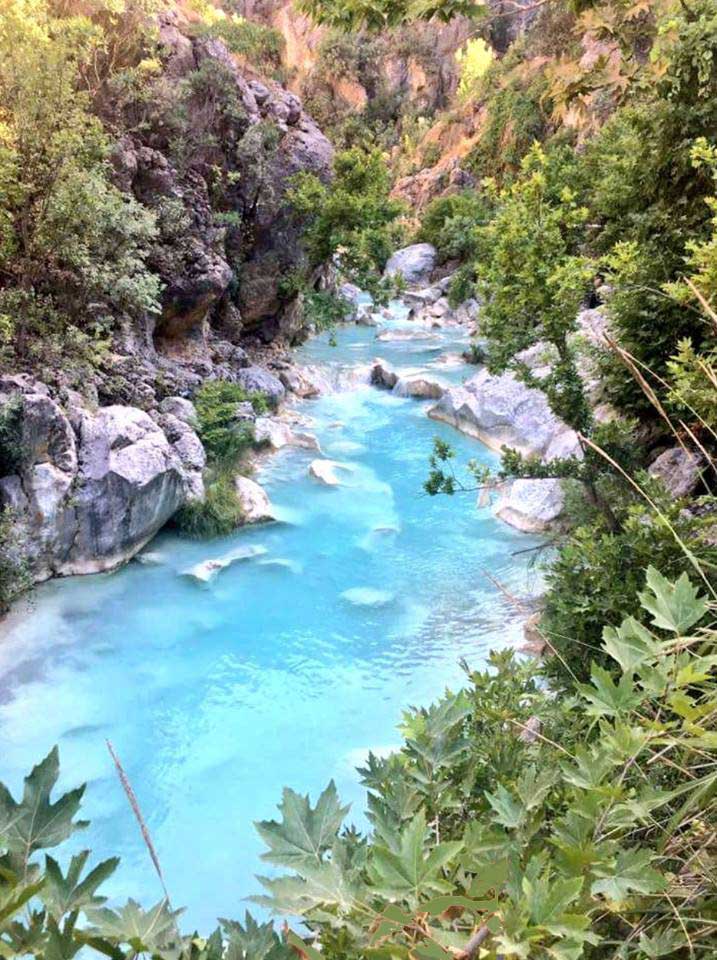

Kurdistan doğası harika bir TABLO gibidir.


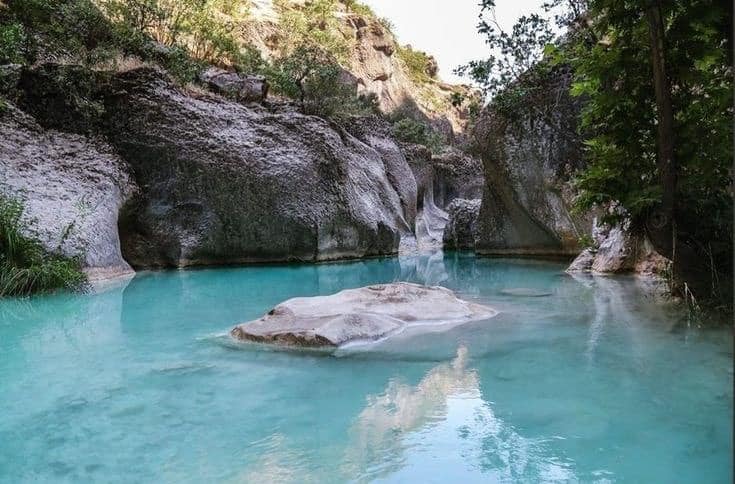
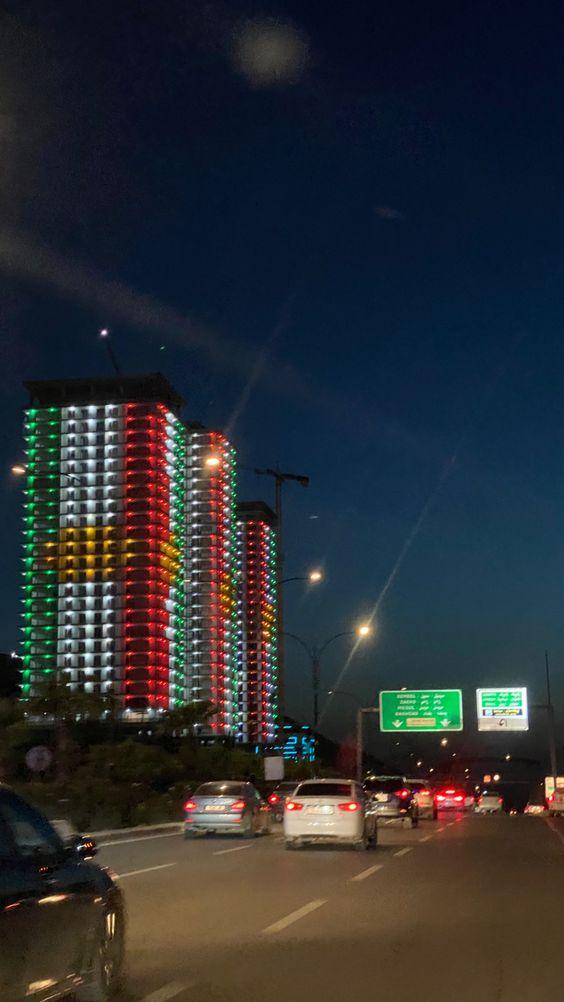
Duhok, Berwarî Bala

Foto: İsmet Mayî
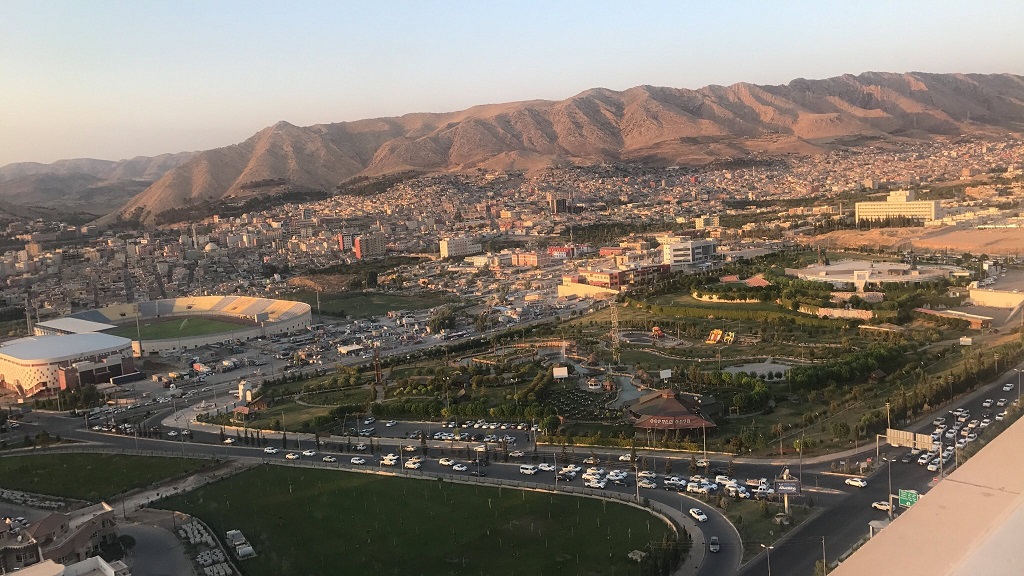


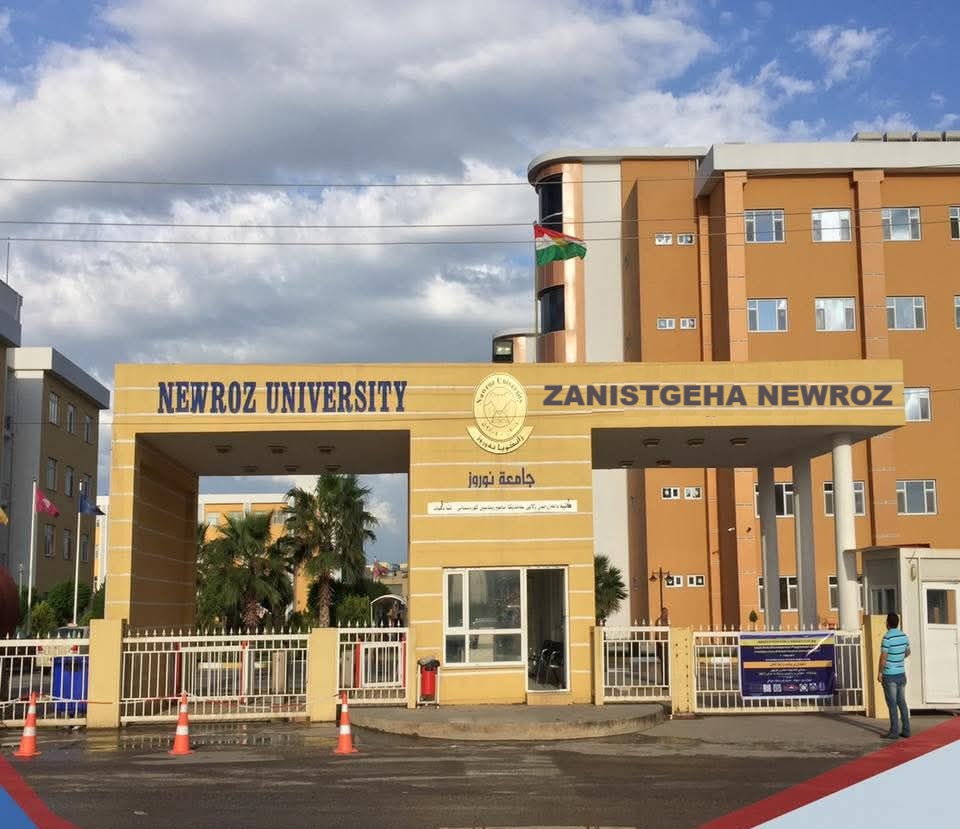
AMERICAN UNIVERSITY OF KURDISTAN

AMERICAN UNIVERSITY OF KURDISTAN Mustafa Barzani Building





Zawîta

Sêmel

Sêmel - Karxaneyeka 1500 sal kevn
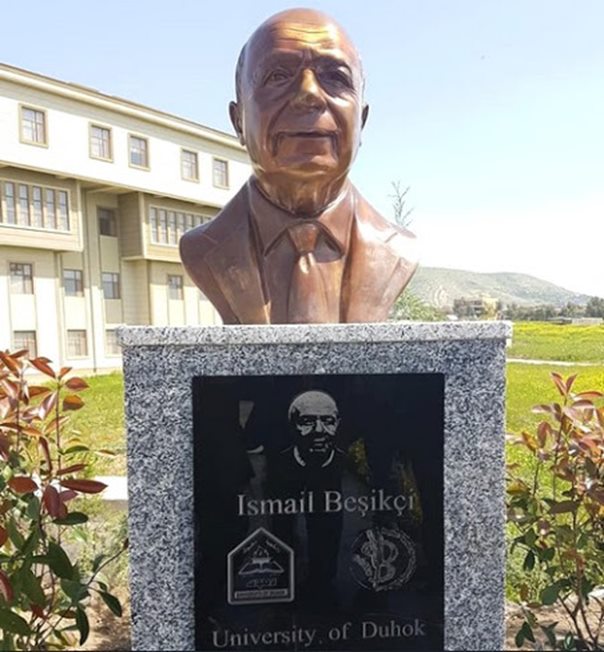






Peyketa Mamoste Îsmaîl Bêşîkçî
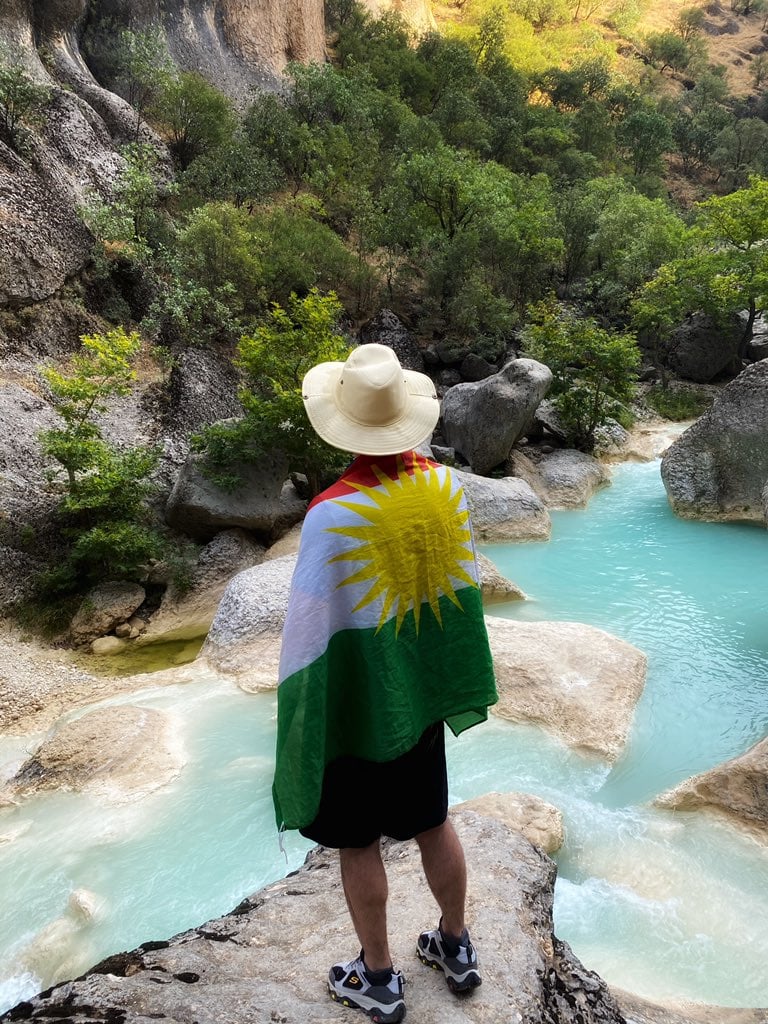



Devera Barzan

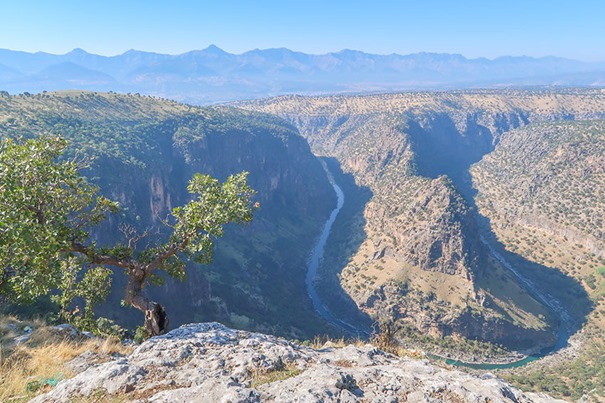
Sersing di navbera Duhok û Amêdiyê de ye, 50 km li dûrî Duhokê ye
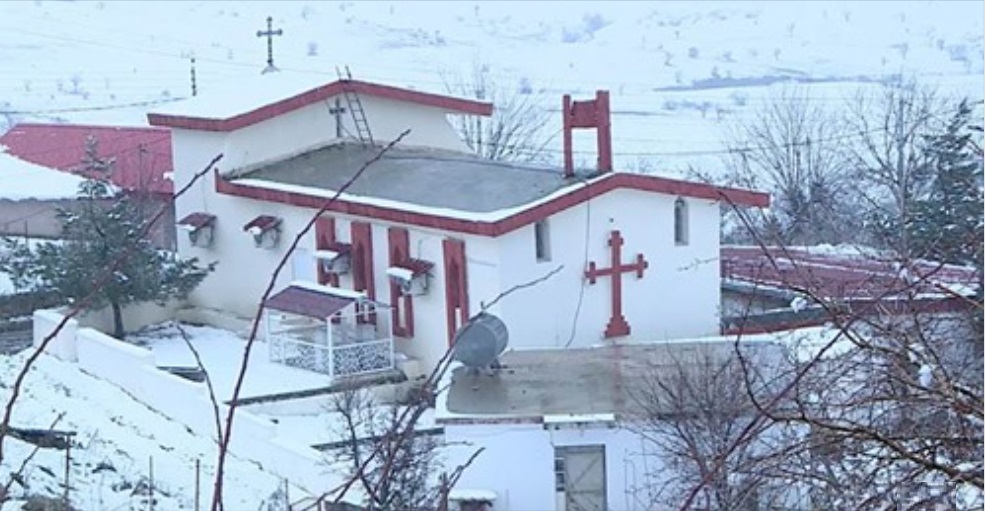

A new church in Southern Kurdistan - Duhok
(Turkey does not allow new church buildings and allows the old ones to decay)



Otomobîlîzm li Kurdistan'ê - Papûra Duhok'ê
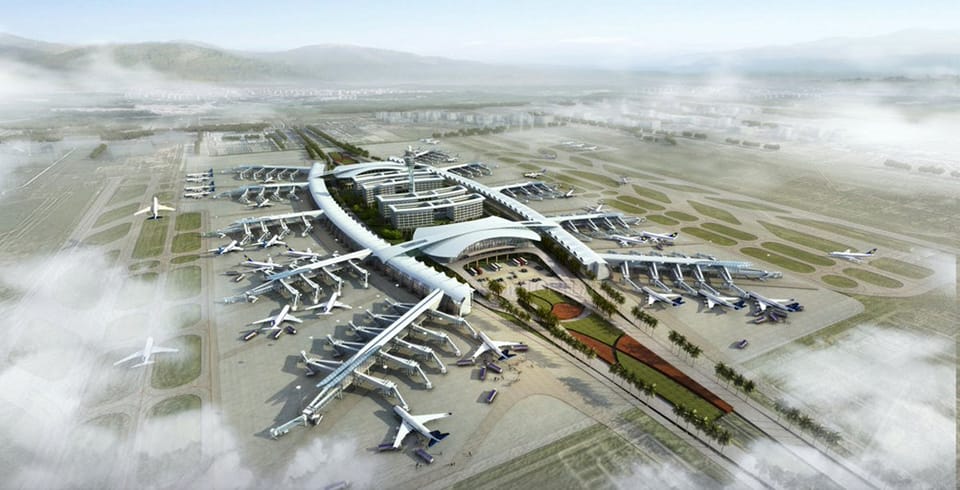

Duhok International Airport Project
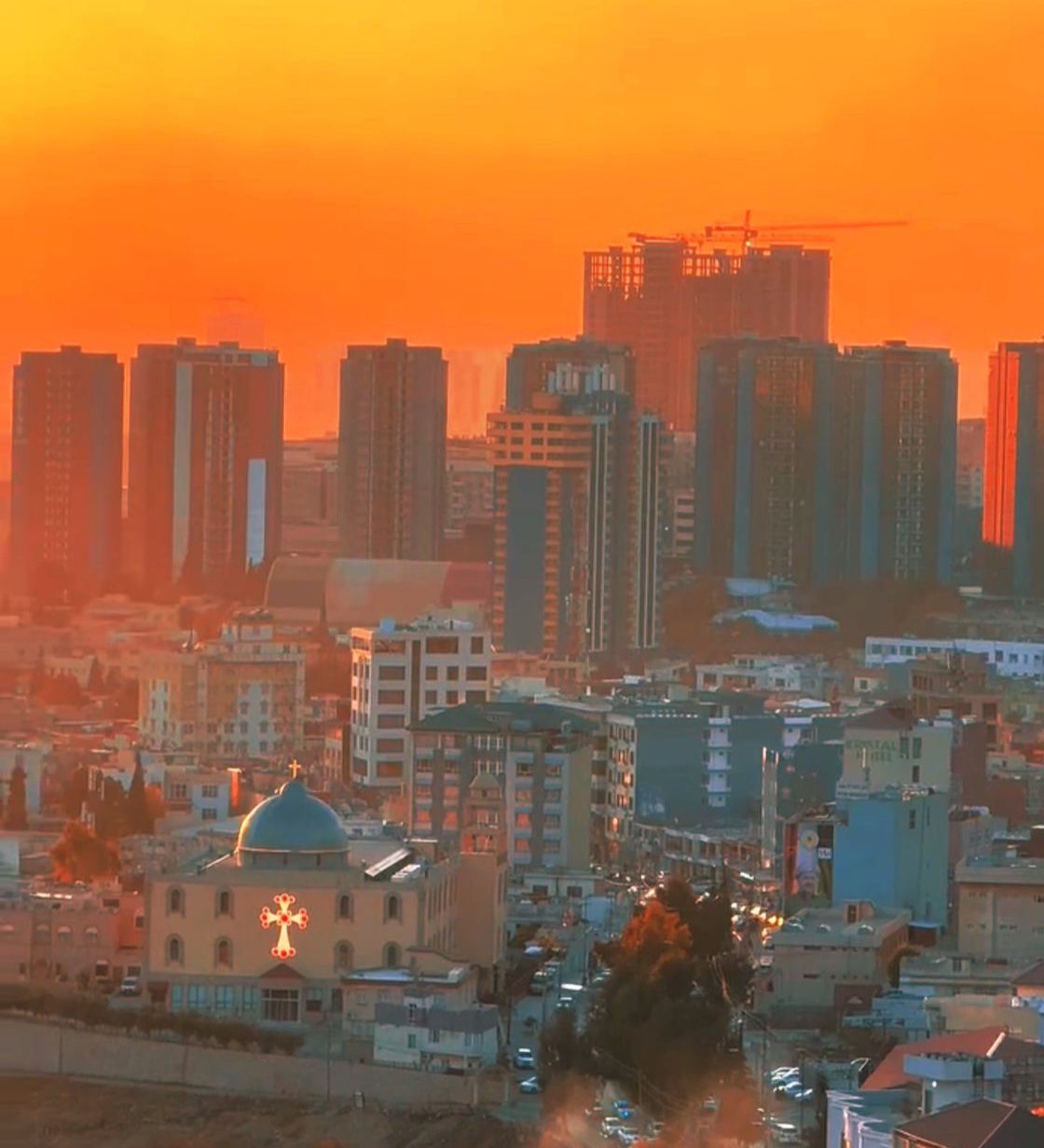



Kürdlerse, yukarıdaki resimde görüldüğü gibi kendi şehirlerinin en gözde, en işlek yerlerinde onlara ibadethane açmalarına müsaade ediyor. Bunu da bir kenara bırakın 2014'te hepimizin gördüğü gibi onları turk-arab ve fars islamist-terörist grupları ISIS, AL-NUSRA, AL-KAIDE, CEPHET-UL-SHAM, HASHD-Î SHABÎ, HİZBULLAH'tan canlarıyla, kanlarıyla koruyor. Bu barbarlar tarafından yıkılan kiliselerini tamir ediyor, yeni kiliseler inşa ediyor. Kürdlerin tarihte ve bugün yardım elini uzattığı bütün bu azınlık gruplar, bugün kürd halkının 1 no'lu düşmanı kesilmişler. Kürdün bir kaşık suda boğulmasını istiyorlar. Kürde şükran borçları olduğu halde, kürdlere karşı kendi cellatları ve kendi katilleri olan işgalci-islamist Türkiye'yi, Irak'ı, Suriye'yi destekliyorlar!! |
ANCAK MAZLUM MAZLUMUN HALİNDEN ANLAR
-- Tarihsel Bellek, Siyasi Vefa ve Kürdlerin Koruyucu Hafızası Ortadoğu tarihinin en sarsıcı gerçeklerinden biri, farklı halkların yaşadığı ortak travmalardır. Soykırımlar, sürgünler ve etnik temizleme politikaları bu coğraflarda yalnızca bir milleti değil, birçok halkı hedef almıştır. Fakat bu ortak acıların karşısında halkların birbirine nasıl yaklaştığı, tarihsel belleğin ne kadar yaşatıldığı ve siyasi vefanın nasıl korunduğu ayrı bir sorudur. “Ancak mazlum mazlumun halinden anlar” özdeyişi bu bağlamda özel bir anlam kazanır. Bu yazıda, özellikle kürd halkının yahudilerle ve Ortadoğu'nun Hristiyan azınlıklarıyla (ermeniler, süryaniler, asurlar) kurduğu tarihsel dayanışma ilişkisi, soykırımlara karşı gösterdiği insani direniş ve günümüz koşullarında yaşanan vefasızlıklar ele alınacaktır. Kürdler ve yahudiler: acının iki kitabı İsrail devleti, mazlum kürd halkına dostane yaklaşan nadir ülkelerden biridir. Bu yakınlığın temelinde stratejik çıkarlar kadar, ortak bir tarihsel hafıza da vardır. Yahudiler, Holokost’ta yaşadıkları felaketi kürdlerin Osmanlı ve yeni türk rejimi altında uğradığı soykırım provaları ve katliamlarla karşılaştırmakta beis görmemektedir. Bu bağlamda İsrail, kürd halkının hem tarihsel dramını tanımakta hem de modern hak mücadelesini desteklemektedir. Kürdler ile yahudiler arasındaki bu bağ, yalnızca devletler arası değil, halklar düzeyinde de “ortak trajediden doğan dayanışma” şeklinde şekillenmektedir. Kürdlerin tarihsel korumacılığı: soykırımın ortasında vicdan 20. yüzyıl başında Osmanlı-türk rejiminin çıkardığı soykırım fermanlarıyla yüz binlerce kürd (1916'daki büyük kürd sürgünü ve katliamını çoğu kürdler bilmiyor hala), ermeni, süryani ve asuri hedef alındı. Buna rağmen birçok kürd ailesi kendi canını riske atarak bu halklardan bireyleri evlerinde sakladı, kaçmalarına yardım etti ya da doğrudan siper oldu. Ermeni kaynaklarında “Kürd komşumuz bizi kurtardı” ifadesi defalarca tekrar edilir. Bu tutum, yalnızca insani değil aynı zamanda politik bir direniştir. Çünkü kürd halkı, kendi halkı gibi zulme uğrayan bir başka halkın katledilmesine izin vermeyerek tarihsel bir etik duruş göstermiştir. Bu gerçek, Ermenistan eski başbakanı Armen Sarkisyan tarafından da 6 Temmuz 2020’de dile getirilmiş, kürd halkına resmi düzeyde teşekkür edilmiştir. Kürdistan'daki Hristiyan azınlıkların ibret verici bir vefasızlık örneği Ne var ki, tarihsel olarak kürd halkının ölümüne koruduğu bu topluluklardan bazılarının günümüzdeki tutumları tam anlamıyla ibret vericidir. Özellikle ermeni, süryani ve asur kilisesi temsilcilerinin büyük bir kısmı, kürdlerin en temel insani haklarına bile karşı çıkarak, doğrudan türk devletinin politikalarını savunmaktadır. Oysa 2014’te DAİŞ ve benzeri islamist türk-arab ve fars terör grupları (ISIS, El-Nusra, Haşd-i Şabî, Hizbullah vs.) bu toplulukları hedef aldığında, onları ölümden kurtaran yine kürd güçleriydi. Binlerce kürd savaşçısı yalnızca kendi halkını değil, bu azınlık gruplarını da canı pahasına korudu. Güney Kürdistan Federe Devleti'nde islamist teröristler tarafından yıkılan kiliseler onarıldı, ibadethaneler yeniden inşa edildi, dini özgürlükler anayasal güvenceye alındı. Ancak bugün, bu halkların temsilcileri kürd şehirlerinde özgürce yaşarken, siyasi platformlarda Türkiye’nin işgalini meşrulaştıran açıklamalar yapabiliyor. Hatta Türkiye tarafından işgal edilen Efrîn ve Serêkaniyê gibi kentlerde kurulan sözde "Hristiyan meclisleri", işgalci türk ordusunun aparatına dönüşmüş durumda. Bu durum yalnızca tarihsel vefasızlık değil, aynı zamanda siyasi ahlaksızlıktır. Kuzey Kürdistan'da kürd dili işgalci islamo-faşist asimilasyoncu-ırkçı türk devleti tarafından yasaklandığı halde, sözümona binyıllardır komşumuz olan ermeniler, asurlar ve süryaniler bize sempati ve destek vereceklerine, onlara kürdçe selam verildiğinde veya kürdçe bir şey sorulduğunda, kürdçe bildikleri halde inatla türkçe cevap veriyorlar ve hatta “falanca kişi kürdçe konuşuyor” diye işgalci islamist türk devletine gidip şikayette bile bulunabiliyorlar. Kürdler, Kürdistan'daki ermeni, süryani, asuri ve diğer azınlık halklara yöneltilmiş saldırı ve haksızlıklar konusunda çok hassas oldukları halde, kürdler katledildiğinde –hem de en barbarca bir şekilde katledildiğinde– bu topluluklardan insanlar, aralarında ne tek bir birey ne de onların hiçbir kuruluşu kürd halkına yapılan bu büyük zulümler karşısında çıt bile çıkarmıyorlar. Bilakis sevindikleri bile müşahade edilmiştir. Bunların kimden taraf oldukları apaçık meydanda değil midir? Ne Halepçe Soykırımı'nda, ne Roboskî ve diğer katliamların ardından, ne bir ermeni, ne bir asuri ve ne de bir süryani birey ya da onların herhangi bir kurumu, kürd halkına karşı işlenen bu büyük insanlık suçlarını kınayan tek bir açıklamada bulunmamıştır. Oysa benzer bir trajedi, tek bir ermeni ya da başka bir hıristiyan bireyin başına geldiğinde, kürd halkı sessiz kalmamıştır. Örneğin ermeni gazeteci Hrant Dink'in islamist türkler tarafından İstanbul'da alçakça katledilmesinin ardından kürdler yıllar boyunca “Em jî Hrant in” (Biz de Hrant’ız) diyerek meydanları doldurmuş, dayanışma göstermiştir. Bu, kürdlerin evrensel adalet ve insan hakları anlayışının, dini ya da etnik kimlikten bağımsız olarak ne kadar güçlü olduğunu gösterir. Kürdlerin demokratik hoşgörüsü ve siyasi şeffaflığı Batı-Kürdistan'ı Rojava başta olmak üzere, Kürdistan’ın birçok bölgesinde azınlık halklar anayasal düzeyde tanınmakta, okullar, medya organları ve ibadet alanları özgürce faaliyet göstermektedir. Süryani okulları kendi dilinde eğitim yapabilmekte, kilise vakıfları uluslararası destek alabilmektedir. Bunun karşısında, bu halkların temsilcilerinin, kürd siyasi hareketine destek olmak yerine, cellatlarıyla iş tutması acı bir çelişkidir. Kürd halkı, hem kendi halkının hem de tarihsel olarak sığındığı halkların onurunu korumaya devam ederken, karşılık olarak ihaneti değil, dayanışmayı beklemektedir. Hafıza, siyaset ve ahlak Tarihsel hafıza, yalnızca geçmişi hatırlamak için değil, bugünü anlamak ve yarını inşa etmek için vardır. Kürdler, tarihin her döneminde mazlum halklara el uzatmış, dini ve etnik fark gözetmeden koruma sağlamıştır. Bugün kürdlere karşı geliştirilen düşmanca tutumlar, yalnızca siyasi değil aynı zamanda ahlaki bir sorundur. “Ancak mazlum mazlumun hâlinden anlar” sözü, hala yol göstericidir. Fakat bu empatiyi sürdürebilmek için, yalnızca kürdler değil, diğer halklar da kendi tarihleriyle yüzleşmeli, vicdani bir tutum almalıdır. Vefa, halkların ahlak testidir. |
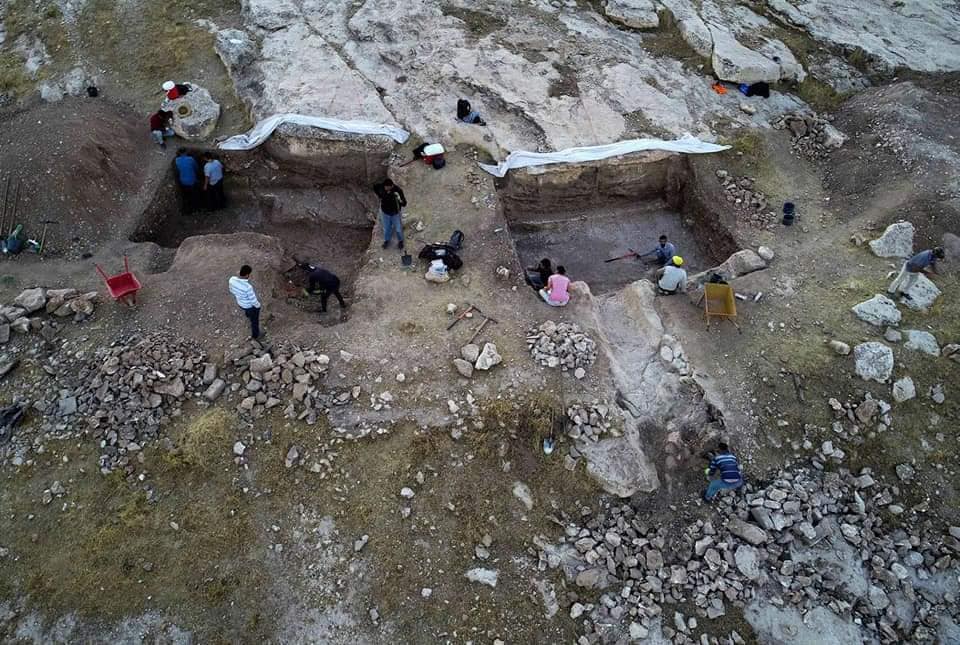
BAJARÊ BABKALÊ KURDA MÎTANNÎ

Bajarê babkalê kurda ku temenê wî 3800 sal e. binavê "Zaxîko" hat dîtin 2022.. Vî bajarî bajar mîtaniyên babkalên kurdan avakiriye.
Cîh:.Sêmêl, gundê Kemûn ê ser çemê Dîclê, sînorê Parêzgeha Duhokê

ZECHEKO BANG KIR ME ..

Tarihin derinliklerinde kadim kürd tarihi su yüzüne çıkıyor...
ZACHEKO BİZİ ÇAĞIRIYOR
ZACHEKO BANG DA
ZECHEKO BANG KIR ME ..
Tarihin derinliklerinde kadim kürd tarihi su yüzüne çıkıyor, 2022
Dicle sularının azalmasının ardından MÖ 3800 Mitanni İmparatorluğu'nun (Almitanip) şehri yeniden gün yüzüne çıktı.
Şehir, Babil metinlerinde geçen "Zacheko" olarak adlandırılır ve çivi yazılı metinlere göre büyük bir çitin yanı sıra bir saray ve birçok bina ve odayı içerir ve ayrıca Mitani İmparatorluğu'nun önemli bir kültür merkezidir.Kurdistan dayika HEMÎ Şaristaniyê ye

-- Berê xwe bidiê!
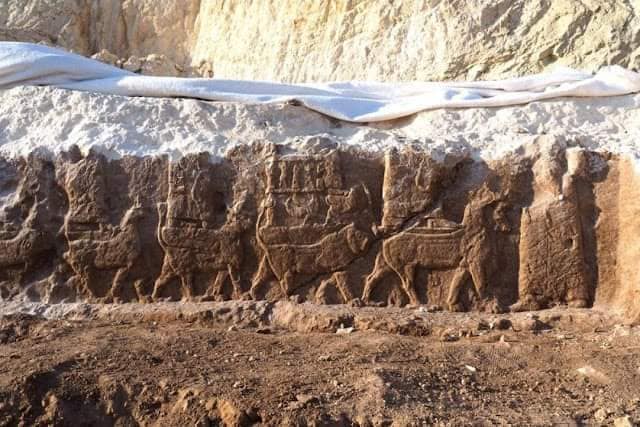
Şarap Presleri ve Duvar resimlerinin keşfi
Kurdistan'ın Duhok ilinde 2.700 yaşında şarap yapım yeri Arleologlar tarafından keşfefildi.
İtalyan ve kürd arkeologlar, Kurdiatan'nın Duhok ilinin iki bölgede bir sulama kanalında, 2.700 yıldan daha eski şarap presleri ve devasa duvar resimlerinin keşfedildiğini duyurdular.
Ortak misyon, Duhok Valiliği'ndeki Xans köyü yakınlarında "endüstriyel şarap presleri" keşfettiğini duyurdu.
İtalya'nın Udine Üniversitesi'nden arkeolog Daniele Morandi-Bonacussi, "Bunun endüstriyel bir şaraphane olduğu anlaşılıyor. Üzümleri şaraba sıkmak için kullanılan 14 tesis bulduk. Bu, türünün ilk keşfi diye açıkladı"
.
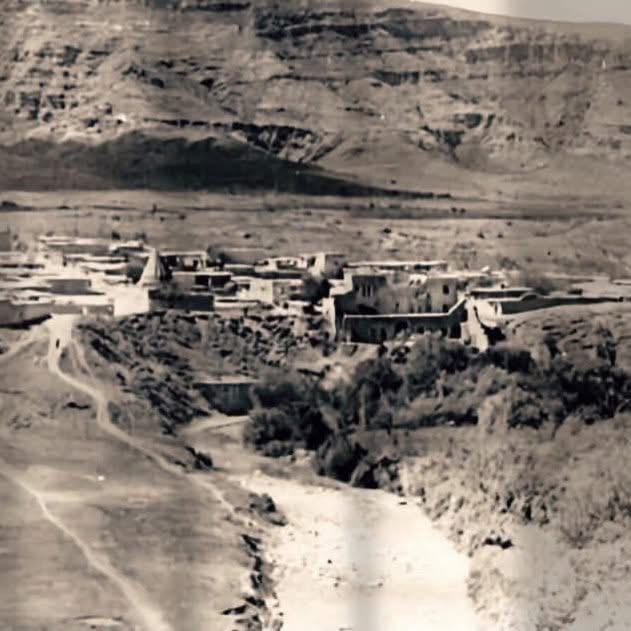


Duhok 1950

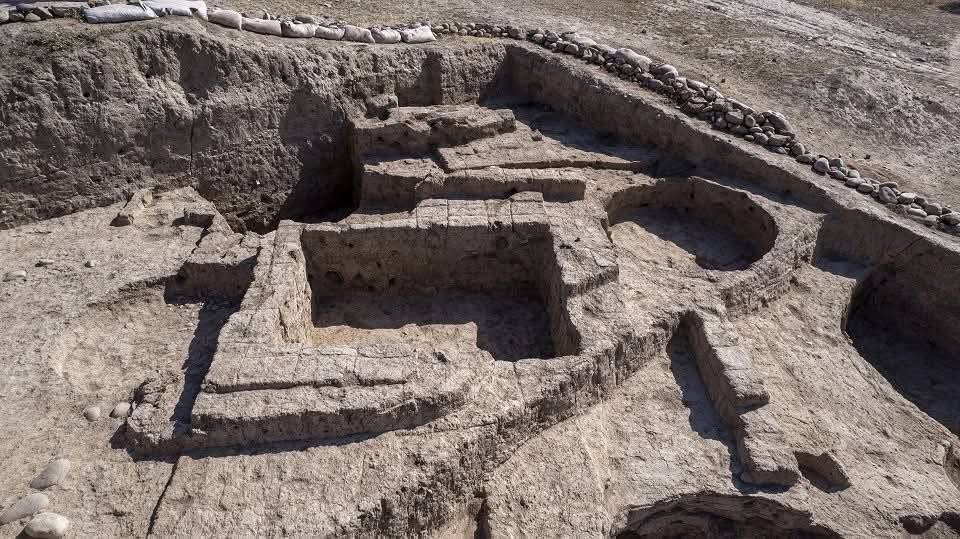
Kurdish and German archaeologists have uncovered a 3,400-year-old Bronze Age palace on the eastern bank of the Tigris River in one of the most important recent archeological finds in the region,

German-Kurdish research team came upon a surprising discovery as ruins emerge from the waters of the Tigris River.The site of Kemune on the eastern Tigris can be dated to the time of the Mittani Empire, which dominated large parts of northern Mesopotamia and Syria from the 15th to the 14th century BCE.The Mittani Empire is a kingdom of the Ancient Near East, but has not received the same levels of attention as other more significant ones. Last autumn, decreasing water levels in the Mosul Dam reservoir due to draughts unexpectedly brought to light remains of an ancient city.The area had been flooded following the construction of the Mosul Dam in the mid-1980s.Archeologists has already discovered the site in 2010, but were unable to excavate it.The Mittani Empire is one of the least researched empires of the Ancient Near East

Almanya ve Kürdistan araştırmacıları, Dicle Nehri'nin Doğu Yakası'nda bulunan ve Kürd Mitani İmparatorluğu'na ait olan, 3600 yıllık ve 2000 metrekarelik
duvar resimleri ve bronz kubbeli bir sarayı keşfetti.
Bu keşfin sebebi, Musul'un kuzeyindeki kuraklık ve alt su tankı seviyelerinin düşmesidir.
Arkeologlar, kuraklık bitmeden önce keşif yerini tam incelemeden için birkaç hafta içinde sarayın tekrar su altında kalabileceğinden korkuyor.

Duhok’ta binlerce yıllık geçmişe sahip Mitaniler dönemine ait antik bir kent bulundu.
Kürdistan Bölgesi’nin Duhok kentinde, 3400 yıllık geçmişe sahip olduğu belirtilen Mitaniler dönemine ait antik bir şehir ortaya çıkarıldı.
Duhok Tarihi Eserleri Müdürlüğü sorumlusu Dr. Hasan Ahmed, düzenlediği basın toplantısında, “Dünya’da ve Duhok’ta ilk kez Mitani uygarlığına ait bir kent ortaya çıkarıldı. Arkeolog ve araştırmacılar, tarihi, milattan önce 1600’lere uzanan bu kentten büyük kazanım ve fayda sağlayacak” dedi.
Çok sayıda antik parça, el yazması ve çivi yazısı kalıntısının bulunduğu antik şehrin Dicle Nehri’nin doğu kıyısında kurulduğunu ve günümüzde Sêmêl ilçesi yakınlarına denk düştüğünü belirten Dr. Ahmed, burada çok sayıda büyük saray ve yapının kalıntılarına rastlandığını ifade etti.
Dr. Ahmed, Duhok Tarihi Eserler Müdürlüğü’nün Alman bilim insanları ile birlikte bu önemli keşfe imza attığını vurguladı.
Düzenlenen basın toplantısında antik kentte bulunan kalıntılar sergilendi.
Almanya’da da bu antik şehrin keşfiyle ilgili bir tanıtım konferansının gerçekleştirilmesi bekleniyor.
26.06.2019
(Kaynak BN)
 |
 |

AncientPages.com | December 14, 2020 | Archaeology, Artifacts, News
AncientPages.com | December 14, 2020 | Archaeology, Artifacts, News
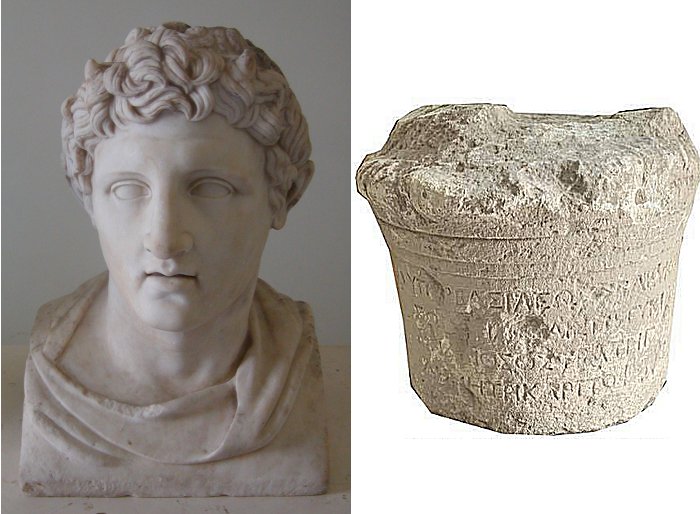
Conny Waters - AncientPages.com - An ancient tablet dated back over 2,000 years was unearthed in Duhok province in northern Kurdistan in March this year, and recently, the artifact was carefully studied by experts.
Ahmed said that "an excavation team from Duhok Museum and Kurdistan Archaeology Organization in March found an antique tablet in Balyuz hills, ten kilometers west of Duhok city, inside the Semel district.""After careful study, we found out that the stone tablet is engraved with Hellenistic script and dates back to 165 BC," the official added.The engravings had been translated into Kurdish by researchers, who also concluded that the inscriptions refer specifically to Demetrius— a Hellenistic-era ruler of the region around the second century B.C.The writing makes references to the period that followed the coming of Alexander the Great, who conquered much of the Middle East, and after his death in 323 BC, the Hellenistic period began to influence Mediterranean history, the process that continued to the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC.
Duhok ("two mountains"), capital of the Duhok Governorate in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq, at the crossroads of three countries: Iraq, Turkey, and Syria, plays an important role as a strategic gateway that connects Kurdistan to the outside world.
Left: Marble portrait bust of Demtetrios I of Macedon (Poliorcetes). Roman copy from 1st century AD of Greek original from 3rd century BC. source; Right: Engraved Kurdistan Tablet dated to more than 2,000 years. Image credit: Department of Antiquities in Kurdistan Region’s Duhok province.Both the city and the surroundings have a population that consists mostly of Kurds, but also minority groups such as Chaldeans, Assyrians, Arabs, and Armenians, mixed in. Duhok is a melting pot of different cultures. Between the 25th and 22nd century BC, it changed hands between the Akkadians, Sumerians, Assyrians, Amorites, Gutians, Hurrians, and Hattians.
Later, it became an integral part of Assyria from the mid 21st century BC until the dissolution of Assyria. Churches can be found throughout the city, and holy Yazidi shrines are located in various parts of the Duhok province. Today, Duhok hosts ancient archaeological sites such as Charstwin Cave (Auskani Empire– 147-226 B. C.), Malta Hill (Assyrian Empire– 900 B.C.), and Halmata Cave (by the Assyrian King Sanharib– 704-681 B.C), to name a few.Several historic sites have already been discovered in Erbil province, the region, to which the earliest historical reference dates to the Third Dynasty of Ur of Sumer when King Shulgi mentioned the city of Urbilum. The city of Erbil was later conquered by the Assyrians.Earlier, Italian and Kurdish archaeologists working at an ancient site in the Kurdistan Region's Duhok province discovered 10 new rock reliefs showing the Assyrian ruler Sargon in the presence of the gods of Assyria, sculpted along a large rock-cut irrigation canal.This discovery of the stone tablet engraved with Hellenistic script will pave the way for researchers to conduct further archaeological investigations in the Kurdistan Region, according to authorities.
Written by Conny Waters - AncientPages.com Staff Writer


Şûnewarekî dîrokî li Ruvia, li tixûbê Duhokê ye ku dîroka wî ya pir kevn e ta 8000 sal pêş vê demê diçe
